Movement of Substance Across the Plasma Membrane
Active transport involves the movement of a substance across the membrane of the absorbing cell against an electrical or chemical gradient. The deformation then pinches off from the membrane on the inside of the cell creating a vesicle containing the captured substance.
Structure Of The Plasma Membrane Article Khan Academy
Secondary active transport involves the use of an.
. People and objects move from one location to another they cross or are contained within certain boundaries and they provide a constant flow as part of larger activity. Cell membrane acts as a barrier to most but not all molecules. In the case of the plasma membrane these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell.
Cell wall In bacteria and plant cells the outermost cell cover present outside the plasma membrane is the cell wall about which we shall study now. The cell membrane is present in all the cells. Light-driven pumps which are found mainly in bacterial cells couple uphill transport to an input of energy from light as with bacterio-rhodopsin discussed in Chapter 10.
The intracellular space and the extracellular space. This is usually to accumulate high concentrations of molecules that a cell needs such as glucose or amino acids. This quiz is all.
By structure it is a porous membrane with pores which permits the movement of selective substances in and out of. Endocytosis is a pathway for internalizing solid particles cell eating or phagocytosis small molecules and. If protein drugs with a molecular mass 20000 gmol are injected IM or sc movement across capillary membranes is so slow that most absorption occurs via the lymphatic system.
The plasma membrane creates a small deformation inward called an invagination in which the substance to be transported is captured. Bacterial cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan. If the cell membrane fails to function normally the cell dies.
Electrolytes in body fluids are active chemicals or cations that carry positive charges and anions that carry negative. The final mechanism for movement across the plasma membrane into the cell is endocytosis a process in which a small patch of plasma membrane encloses particles or tiny volumes of fluid that are at or near the cell surface. Figure 81 Despite its seeming hustle and bustle Grand Central Station functions with a high level of organization.
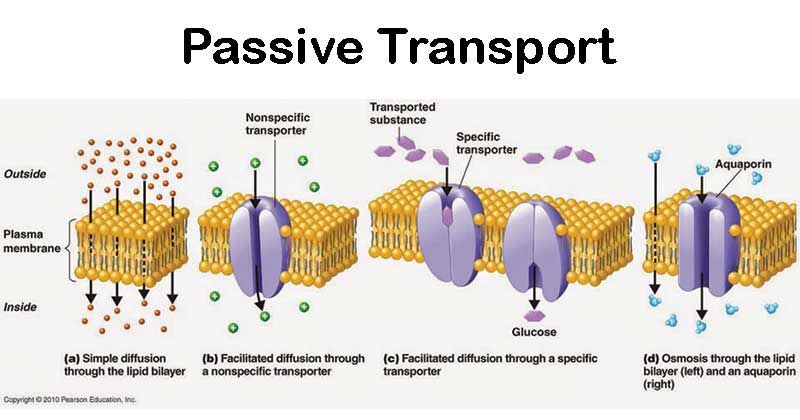
Diffusion Passive Transport 2. If the process uses chemical energy such as adenosine triphosphate ATP it is called primary active transport. For instance take two flasks and fill one with a mild sugar solution and the other with a.
The membrane enclosure then sinks into the cytoplasm and pinches off from the membrane forming a vesicle that moves into the cytoplasm. Fluid and electrolyte balance is a dynamic process that is crucial for life and homeostasis. Cell Membrane.
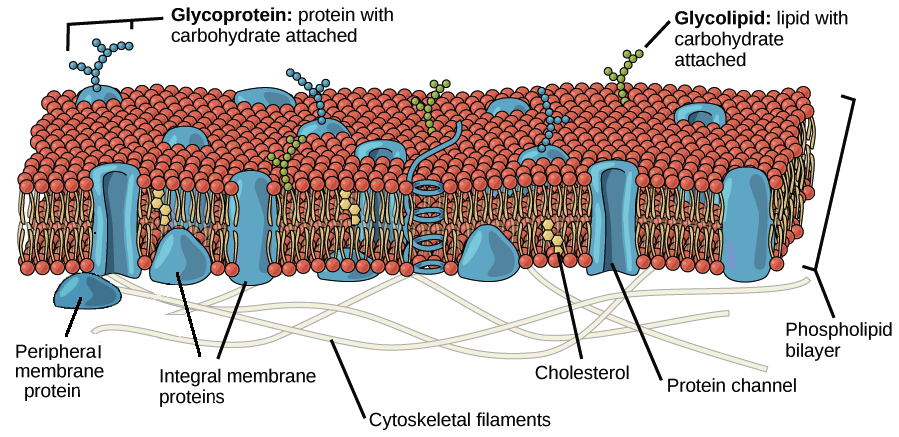
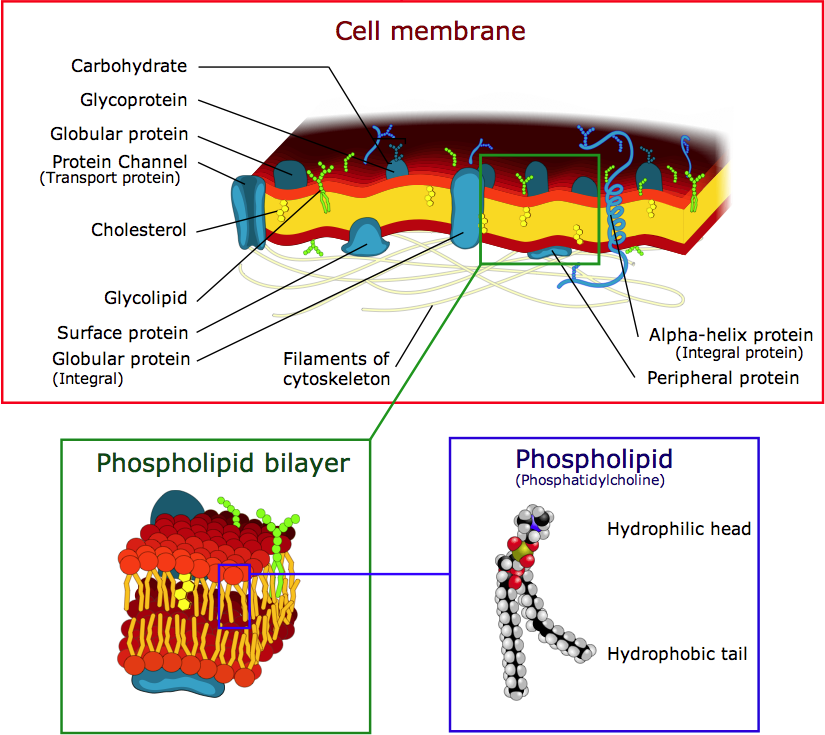
The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments. Proteins embedded within the phospholipid bilayer. The cell membrane or plasma membrane is the structure that keeps cytoplasm from spilling out of a cell.
Such movement across the membrane is aided by the electric charge and pH. Coupled carriers couple the uphill transport of one solute across the membrane to the downhill transport of another. Exocytosis is an important process of plant and animal cells as it performs the opposite function of endocytosisIn endocytosis substances that are external to a cell are brought into the cell.
Cell transport refers to the movement of substances across the cell membrane. This membrane is composed of phospholipids which form a lipid bilayer that separates the contents of a cell from the extracellular fluidThe lipid bilayer is semi-permeable meaning that only certain molecules are able to diffuse across the. Transport across cell membrane is classified into four ways.
Fluid occupies almost 60 of the weight of an adult. ATP-driven pumps couple uphill transport to the hydrolysis of ATP. The journals editor Yasmin Khakoo MD FAAN in conjunction.
Pediatric Neurology publishes timely peer-reviewed clinical and research articles covering all aspects of the developing nervous systemPediatric Neurology features up-to-the-minute publication of the latest advances in the diagnosis management and treatment of pediatric neurologic disorders. The flow of water through a semi-permeable membrane is referred to as osmosis. This process requires energy and is at risk of competitive inhibition by other.
Cell membrane regulates movement of substance into and out of the cell. Exocytosis is the process of moving materials from within a cell to the exterior of the cell. The cell membranes four primary functions include cell signaling selective transport excretion of wastes and structural support.
It is also referred to as the plasma membrane. Active transport is the movement of a substance across a membrane against its concentration gradient. Typically water is the sole free-flowing molecule across this barrier.
That is the substance is temporarily bound to another substance that transports it across the cell membrane where it is released. Body fluid is located in two fluid compartments. The cell membrane is the outer covering of a cell within which all other organelles such as the cytoplasm and nucleus are enclosed.
It is a selective process meaning that only certain molecules and ions are allowed to pass through the membrane. However other molecules are unable to pass through the membrane. Analogously a plasma membranes functions involve movement within the cell and across.
Since the cell membrane is. This process requires energy and is therefore a type of active transport. It is often described as the plasma membrane.
It is the passive movement of molecules along a concentration gradient. It is a thin flexible coating around the cells of all living things. Cell membranes are semi-permeable barrier separating the inner cellular environment from the outer cellular environment.
Like all other cellular membranes the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. Because the membrane does not allow all molecules to pass through it osmosis is a selective process. In such cases drug delivery to systemic circulation is slow and often incomplete because of first-pass metabolism metabolism of a drug before it reaches systemic circulation by proteolytic.
Chapter 7 Transport Across Cellular Membranes In Fundamentals Of Cell Biology On Openalg

Chapter 3 Movement Of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane Diagram Quizlet

Cell Transport Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation

Cell Membranes Learn Science At Scitable
0 Response to "Movement of Substance Across the Plasma Membrane"
Post a Comment